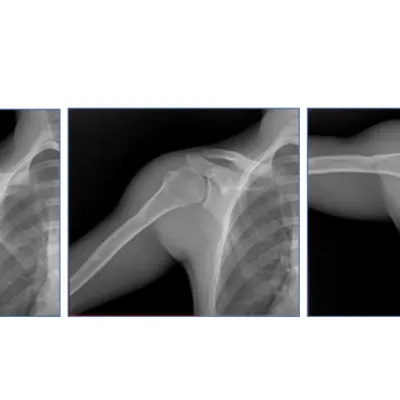
Dynamic Digital Radiography (DDR)
See Radiology Like Never Before.
Dynamic Digital Radiography is the next generation of medical imaging. Unlike static X-rays, this novel, low-dose motion X-ray technology allows clinicians to visualize anatomy in motion.
DDR acquires up to 15 sequential radiographs per second, creating a "cine loop" that reveals complete physiological cycles. By bridging the gap between standard X-ray and CT/MRI, DDR provides a cost-effective solution for diagnosing musculoskeletal injuries and respiratory pathologies without the high radiation dose of fluoroscopy.
Seamless Integration with Konica Minolta Systems.
DDR is FDA-cleared and available on our KDR® Flex OTC, KDR® Advanced U-Arm, and mKDR Xpress® systems.
DDR received the Vizient Innovative Technology Designation!
Konica Minolta’s Dynamic Digital Radiography (DDR) has received Vizient’s Innovative Technology designation—an honor that recognizes breakthrough innovations advancing clinical care, patient safety, and healthcare efficiency. This distinction underscores DDR’s impact in transforming the way healthcare providers deliver imaging and care.
Why Choose Dynamic Digital Radiography?
- Fast, Efficient Exams: In less than a minute, DDR captures up to 20 seconds of physiological movement. The system is operator-friendly, allowing radiology staff to perform exams without a physician present.
- Low-Dose Patient Safety: DDR creates diagnostic-quality motion sequences with significantly lower radiation exposure than average fluoroscopy exams, making it safer for repeat studies.
- Versatile Patient Positioning: Perform weight-bearing X-rays and motion studies with the patient standing, seated, or on a table. This flexibility is critical for accurate orthopedic diagnosis and for assessing spine stability.
- PACS agnostic
- Dose equivalent to about 2 standard X-rays
- Short exposure time for optimal productivity
- Synchronized multi-frame acquisition
- Multi-function X-ray system for dynamic and static images for cost and workflow effectiveness
- Up to 300 images acquired over 20 seconds creates a “cine-loop”
Clinical Applications of DDR Technology
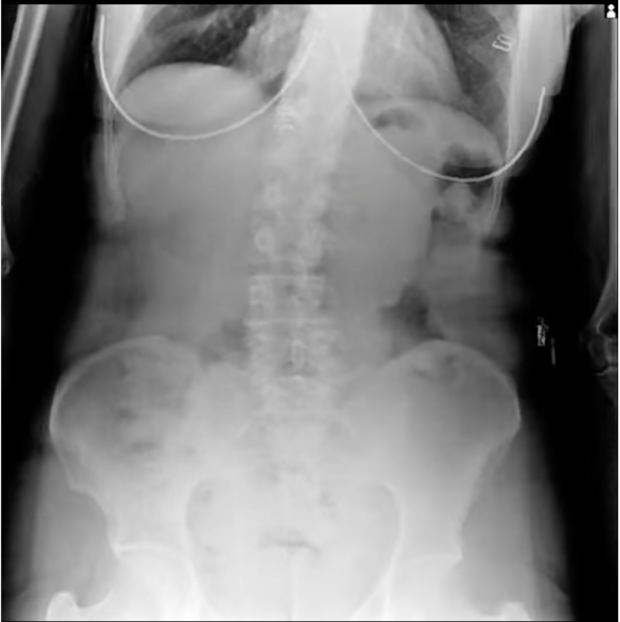
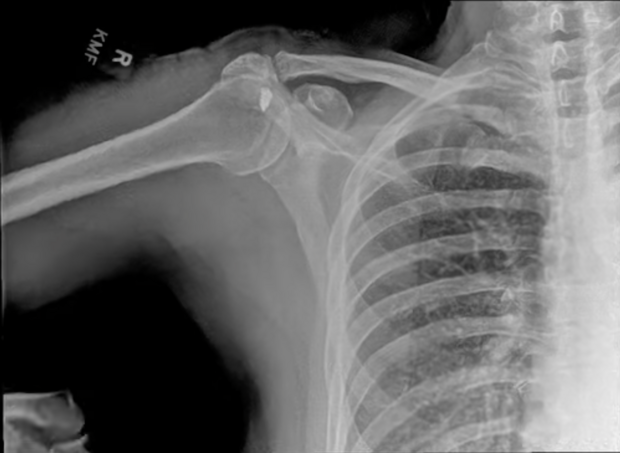
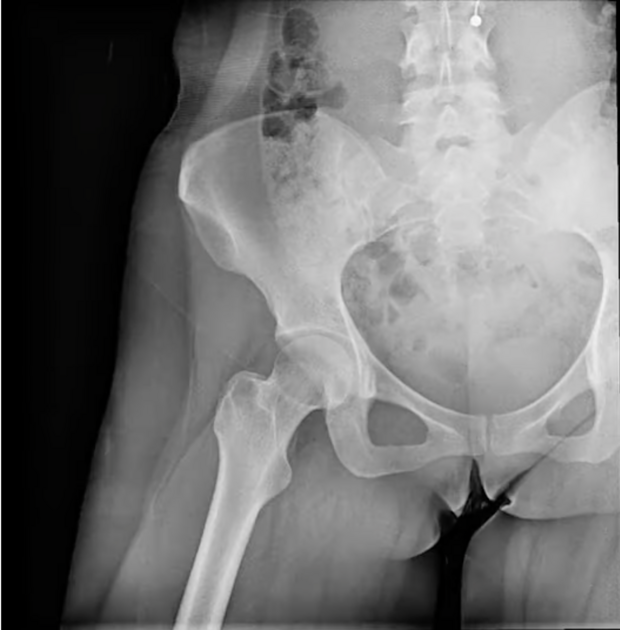
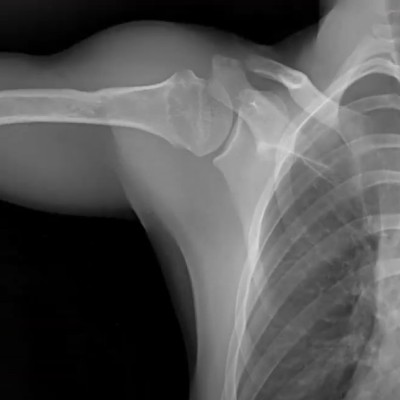
Musculoskeletal & Orthopedic Applications
DDR transforms orthopedic diagnostics by presenting bone and soft tissue in motion. Unlike static X-rays, DDR allows orthopedists to visualize joint stability and kinematics in weight-bearing positions. This is critical for diagnosing whiplash, impingement syndromes, and ligament instability.
Upper Extremities
Lower Extremities
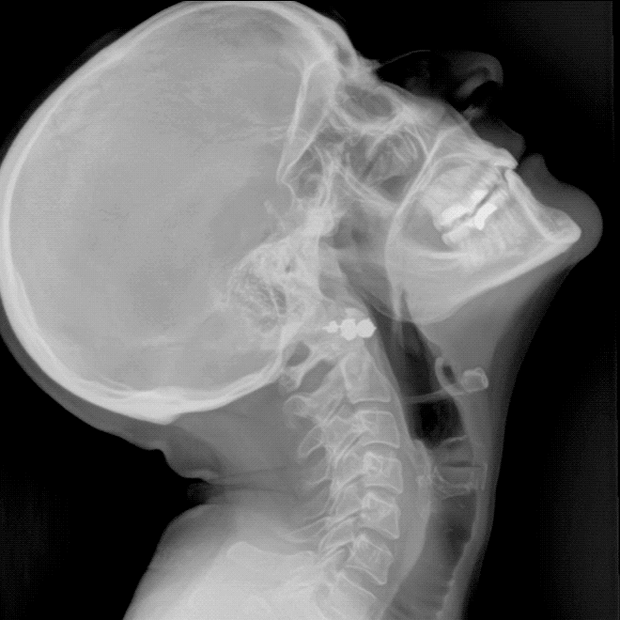
Cervical & Lumbar Spine Stability
Assess spine stability with a detailed view of the full range of motion. DDR captures flexion and extension sequences to identify instability that static X-rays and MRI often miss.
C-Spine
L-Spine
Swallow, Speech Pathology, and Post-Bariatric Sleeve Studies
Enhance dysphagia assessment using DDR with radiolucent contrast. This provides a high-frame-rate visualization of the swallowing mechanism (deglutition) and esophageal motility, offering a low-dose alternative to traditional fluoroscopy for speech pathology studies.
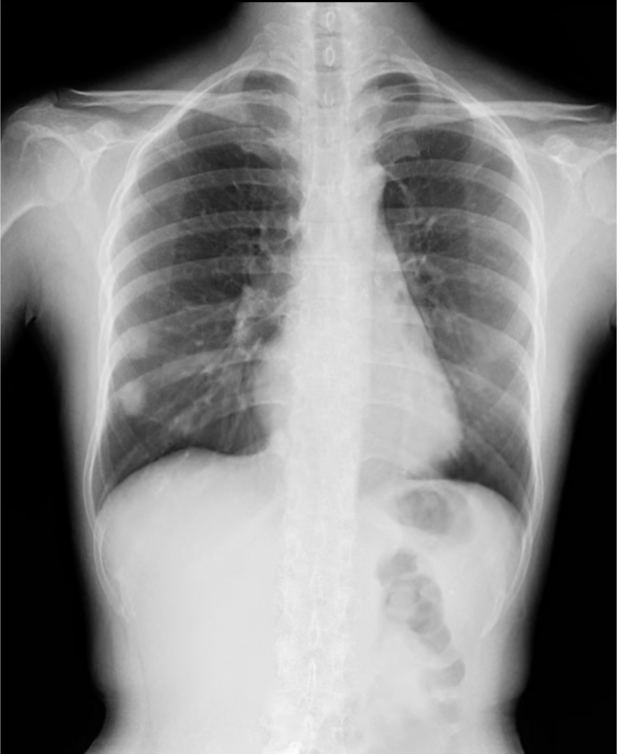
Thoracic DDR & Dynamic Chest Radiography
Chest radiography is the standard for assessing respiratory health, but static images often tell only half the story. DDR allows clinicians to observe lung function and diaphragm motion. By visualizing the physiological cycle, DDR enables rapid diagnosis of COPD, asthma, and diaphragm paralysis.
Increasing Clinical Value with DDR
Operational Advantages
- Fast, Efficient Workflow: In less than a minute, the system acquires up to 20 seconds of physiological movement. These exams can be performed by standard radiology staff without a physician's presence, maximizing departmental throughput.
- Low-Dose Patient Safety: DDR provides diagnostic motion video at a significantly lower radiation dose than an average fluoroscopy exam, making it a safer option for pediatric patients and frequent follow-ups.
- Convenient & Versatile: A true 2-in-1 solution, the system performs all standard static X-rays as well as motion studies. Images can be acquired with the patient standing, seated, or on a table to replicate real-world symptoms.
Assessing Spine Stability and Joint Motion
Standard X-ray exams are limited to static views of the spine in flexed and extended positions, often missing the pathology that occurs between those points.
DDR revolutionizes this process by providing a detailed view of the whole kinematic chain. Many orthopedic facilities are adopting DDR to:
- Diagnose Stability & Biomechanics: Visualize joint space and identify sources of pain or "clicking" in motion.
- Assess Injury: improved visualization for conditions like whiplash and ligament instability.
- Treatment Follow-up: Evaluate postoperative movement before ordering expensive advanced modalities like CT or MRI.
Furthermore, showing patients their own joint movement in video format makes doctor-patient communication simpler and more effective, improving patient satisfaction scores.
The Experts Speak
DDR Uses in Pulmonology
DDR Uses in Orthopedics
In the Press
Recent Scientific Papers
-
Noriaki Wada Assessment of pulmonary function in COPD patients using dynamic digital radiography: A novel approach utilizing lung signal intensity changes during forced breathing. European Journal of Radiology
-
Yuzo Yamasaki Diagnostic accuracy and added value of dynamic chest radiography in detecting pulmonary embolism: A retrospective study. European Journal of Radiology Open
-
Ziyang Xia Investigation of diaphragmatic motion and projected lung area in diaphragm paralysis patients using dynamic chest radiography. Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery